Lesson 1 addition properties and subtraction rules – Embark on an educational journey with Lesson 1: Addition Properties and Subtraction Rules, where the fundamental concepts of mathematics unfold, promising a transformative understanding of numerical operations.
This lesson delves into the intricate world of addition properties, unraveling the secrets of the commutative, associative, and identity properties. It further illuminates the relationship between addition and subtraction, empowering learners to navigate numerical challenges with confidence.
1. Definition and Overview of Addition Properties: Lesson 1 Addition Properties And Subtraction Rules

Addition properties in mathematics are fundamental rules that govern the operation of adding numbers. These properties provide a framework for simplifying expressions, performing calculations efficiently, and understanding the relationships between numbers.
1.1. Commutative Property of Addition
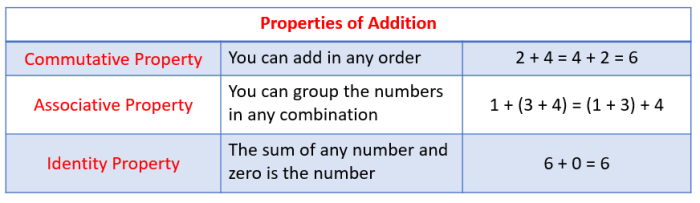
The commutative property of addition states that the order of addends (numbers being added) does not affect the sum. In other words, a + b = b + a for any real numbers a and b.
Examples:
- 2 + 5 = 5 + 2 = 7
- -3 + 7 = 7 + (-3) = 4
1.2. Associative Property of Addition
The associative property of addition states that the grouping of addends within a sum does not affect the sum. In other words, (a + b) + c = a + (b + c) for any real numbers a, b, and c.
Examples:
- (2 + 5) + 3 = 2 + (5 + 3) = 10
- (-3 + 7) + 2 = -3 + (7 + 2) = 6
1.3. Identity Property of Addition
The identity property of addition states that the sum of any number and zero is the number itself. In other words, a + 0 = a for any real number a.
Examples:
- 2 + 0 = 2
- -5 + 0 = -5
The identity property plays a significant role in mathematical operations, as it ensures that the sum of any number and zero remains unchanged.
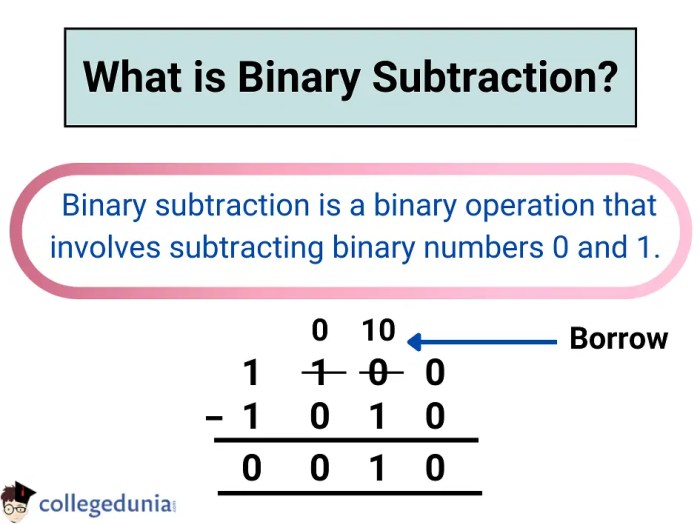
2. Subtraction Rules
Subtraction is the inverse operation of addition. The relationship between addition and subtraction can be expressed using the following rules:
2.1. Rule for Subtracting a Number from a Sum
To subtract a number from a sum, add the additive inverse of that number. The additive inverse of a number is the number that, when added to the original number, results in zero.
Example:
To subtract 3 from the sum of 5 and 2, we add the additive inverse of 3, which is -3:
5 + 2 – 3 = 5 + (-3) + 2 = 4
2.2. Rule for Subtracting a Sum from a Number, Lesson 1 addition properties and subtraction rules
To subtract a sum from a number, add the additive inverse of that sum. The additive inverse of a sum is the number that, when added to the original sum, results in zero.
Example:
To subtract the sum of 3 and 5 from 10, we add the additive inverse of 3 + 5, which is -8:
10 – (3 + 5) = 10 + (-8) = 2
Answers to Common Questions
What is the commutative property of addition?
The commutative property states that the order of addends does not affect the sum.
How does the associative property simplify expressions?
The associative property allows us to group numbers in different ways without changing the result, making it easier to simplify complex expressions.
What is the significance of the identity property in mathematics?
The identity property states that adding zero to any number does not change its value, highlighting the unique role of zero in mathematical operations.