Unveiling the secrets of acids and bases, this guide unveils the captivating world of color by number acids and bases answers. Delving into the fascinating realm of chemistry, this narrative explores the intricate relationship between colors and the fundamental properties of these substances.
As we embark on this journey, we will unravel the mysteries of pH values, unravel the complexities of the Arrhenius theory, and venture into the depths of advanced concepts, leaving no stone unturned in our quest for knowledge.
1. Understanding Color by Number Acids and Bases
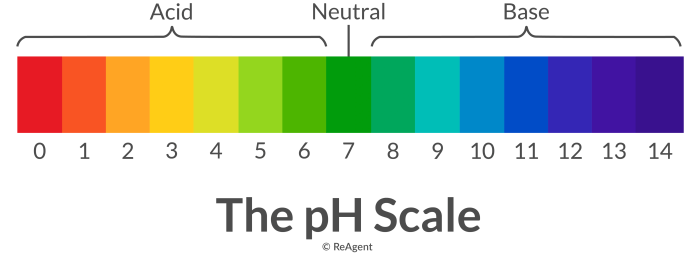
Color by number acids and bases is a method of identifying acids and bases using a color-coded scale. The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity or basicity, and it is represented by a number on a scale from 0 to 14. Acids have a pH below 7, while bases have a pH above 7.
Color by number acids and bases uses a series of colors to represent different pH values. For example, red is used to represent acids, blue is used to represent bases, and green is used to represent neutral solutions. This color-coding makes it easy to identify acids and bases at a glance.
Color by number acids and bases is a simple and effective way to identify acids and bases. However, it is important to note that it is not a perfect method. Some acids and bases may not have a distinct color, and the color of a solution can be affected by other factors, such as the presence of impurities.
Advantages of Using Color by Number Acids and Bases
- Simple and easy to use
- Can be used to identify acids and bases quickly and easily
- Can be used to teach students about acids and bases
Limitations of Using Color by Number Acids and Bases, Color by number acids and bases answers
- Not a perfect method
- Some acids and bases may not have a distinct color
- The color of a solution can be affected by other factors
- Red: Acidic
- Green: Neutral
- Blue: Basic
- Titrations: Color by number acids and bases can be used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base.
- Acid-base reactions: Color by number acids and bases can be used to study acid-base reactions and to determine the products of these reactions.
- pH testing: Color by number acids and bases can be used to test the pH of biological fluids, such as blood and urine.
- Enzyme activity: Color by number acids and bases can be used to study enzyme activity and to determine the optimal pH for enzyme activity.
- Water quality monitoring: Color by number acids and bases can be used to monitor the pH of water and to detect pollution.
- Soil testing: Color by number acids and bases can be used to test the pH of soil and to determine the suitability of soil for growing plants.
2. Acids and Bases
Definition of Acids and Bases According to the Arrhenius Theory
According to the Arrhenius theory, an acid is a substance that produces hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. A base is a substance that produces hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water.
Properties of Acids and Bases
Acids are typically sour, corrosive, and can react with metals to produce hydrogen gas. Bases are typically bitter, slippery, and can react with acids to produce salts and water.
Examples of Common Acids and Bases
Some common acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and nitric acid (HNO3). Some common bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).
3. Color by Number Acids and Bases Answers
Color-Coded Table of pH Values
| pH Value | Color |
|---|---|
| 0-6 | Red |
| 7 | Green |
| 8-14 | Blue |
Key to the Color-Coded Table
How to Use the Color-Coded Table to Identify Acids and Bases
To use the color-coded table to identify acids and bases, simply compare the pH of the solution to the colors in the table. If the pH is below 7, the solution is acidic. If the pH is 7, the solution is neutral.
If the pH is above 7, the solution is basic.
4. Applications of Color by Number Acids and Bases
Chemistry
Color by number acids and bases are used in a variety of chemistry applications, such as:
Biology
Color by number acids and bases are used in a variety of biology applications, such as:
Environmental Science
Color by number acids and bases are used in a variety of environmental science applications, such as:
5. Advanced Concepts in Color by Number Acids and Bases
Limitations of the Arrhenius Theory
The Arrhenius theory is a simple and useful model for understanding acids and bases. However, it has some limitations. For example, the Arrhenius theory does not explain the behavior of acids and bases in non-aqueous solutions.
Brønsted-Lowry Theory and the Lewis Theory of Acids and Bases
The Brønsted-Lowry theory and the Lewis theory of acids and bases are two more general theories that can be used to explain the behavior of acids and bases in both aqueous and non-aqueous solutions.
The Brønsted-Lowry theory defines an acid as a substance that can donate a proton (H+), and a base as a substance that can accept a proton. The Lewis theory defines an acid as a substance that can accept an electron pair, and a base as a substance that can donate an electron pair.
How These Theories Expand Our Understanding of Acids and Bases
The Brønsted-Lowry theory and the Lewis theory of acids and bases expand our understanding of acids and bases in several ways. First, these theories show that acids and bases can exist in both aqueous and non-aqueous solutions. Second, these theories show that acids and bases can be classified according to their ability to donate or accept protons or electrons.
FAQ Resource
What is the significance of color in identifying acids and bases?
Color plays a crucial role in identifying acids and bases, as it is directly linked to their pH values. Different pH values correspond to specific colors, allowing for quick and easy identification using color-coded charts.
How does the Arrhenius theory define acids and bases?
According to the Arrhenius theory, acids are substances that produce hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water, while bases produce hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water.
What are the limitations of the Arrhenius theory?
The Arrhenius theory has limitations as it only applies to aqueous solutions and does not account for non-aqueous acid-base reactions.